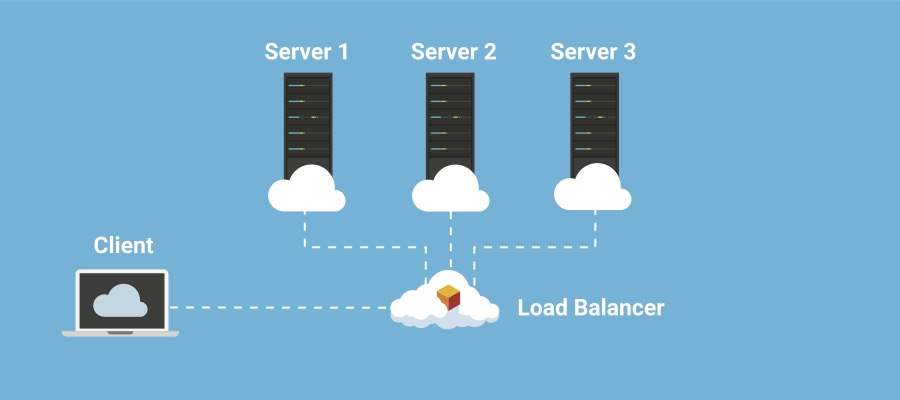
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services over the internet, allowing users to access and use a wide range of resources, including servers, storage, databases, software applications, and networking, without the need for on-premises infrastructure. The term “cloud” in cloud computing symbolizes the internet, representing a virtual space where data and applications are stored and processed.
Cloud computing offers several benefits, including scalability, flexibility, cost-efficiency, and reliability. Users can easily scale their resources up or down based on demand, paying only for the services they use. The cloud provides flexibility by allowing users to access their applications and data from anywhere, using any device with an internet connection. It also eliminates the need for companies to invest in and maintain their own physical infrastructure, reducing costs and freeing up resources for other business priorities. Cloud computing providers typically ensure high levels of reliability, with built-in redundancy and disaster recovery capabilities.
There are three main types of cloud computing services:
-
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. Users can rent virtual machines, storage, and networks to build their own IT infrastructure. This allows businesses to have more control and flexibility in managing their applications and systems.
-
Platform as a Service (PaaS): PaaS offers a platform and environment for developers to build, test, and deploy applications. It provides a complete development and deployment environment, including operating systems, databases, and development tools. PaaS allows developers to focus on coding and application logic without worrying about underlying infrastructure.
-
Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. Users can access and use software applications hosted in the cloud, eliminating the need for installation and maintenance. Examples of SaaS include web-based email, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, and collaboration tools.
In addition to these three types, there are hybrid cloud solutions that combine elements of public and private clouds, allowing organizations to leverage the benefits of both while maintaining control over sensitive data and applications.
Overall, cloud computing revolutionizes the way businesses and individuals access and utilize computing resources, enabling greater efficiency, flexibility, and scalability in the digital era.